[SAR ADC] 논문 : Monotonic Capacitor Switching Procedure - 3. Implementation of Key Building Blocks
A 10-bit 50-MS/s SAR ADC With a Monotonic Capacitor Switching Procedure
모노톤 커패시터 스위칭 절차를 적용한 10비트 50MS/s SAR ADC
이전 글 : https://brush-up.tistory.com/243
Implementation of Key Building Blocks
The fundamental building blocks of the proposed ADC are a S/H circuit, a dynamic comparator, SAR control logic, and a capacitor network. The design considerations of the building blocks are described in the following subsections.
제안된 ADC의 기본 구성 요소는 S/H(샘플 앤 홀드) 회로, 동적 비교기, SAR(연속 근사 레지스터) 제어 논리 및 커패시터 네트워크입니다. 각 구성 요소의 설계 고려 사항은 다음 소단락에서 설명됩니다.
A. S/H Circuit
A. S/H Circuit
The bootstrapped switch [14] shown in Fig. 7(a) performs the S/H function. With the bootstrapped switch, the gate-source voltage of the sampling transistor is fixed at the supply voltage (VDD), which makes the on-resistance a small constant value and thus improves the switch linearity. When the bootstrapped switch is off, the input signals couple to the sampling capacitors through the Cds (around 5 fF) which is composed by the drain-source capacitor of the sampling transistor and the routing parasitic capacitance. The coupling effect degrades the high frequency performance because Cds induces unequal charges in the comparison cycles, which results in a dynamic offset. Therefore, two cross-coupled metal-oxide-metal (MOM) capacitors (around 5 fF) are used to neutralize the effect [see Fig. 7(b)]. The two cross-coupled capacitors reduce the coupling effect to less than 1/2 LSB (2.5 fF) in the 10-bit case under processing variation. To achieve higher precision, dummy switches and dummy routing are alternative solutions to reduce the coupling effect.
A. S/H 회로
그림 7(a)에 표시된 부트스트랩 스위치 [14]는 S/H(샘플 앤 홀드) 기능을 수행합니다. 부트스트랩 스위치를 사용하면 샘플링 트랜지스터의 게이트-소스 전압이 공급 전압(VDD)에 고정되어 온-저항이 작은 일정한 값이 되어 스위치의 선형성이 향상됩니다. 부트스트랩 스위치가 꺼져 있을 때, 입력 신호는 샘플링 커패시터에 Cds(약 5 fF)를 통해 결합됩니다. 이는 샘플링 트랜지스터의 드레인-소스 커패시터와 라우팅 기생 커패시터로 구성됩니다. 이 결합 효과는 Cds가 비교 주기에서 불균일한 전하를 유도하여 동적 오프셋을 발생시키기 때문에 고주파 성능을 저하시킵니다. 따라서, 두 개의 상호 연결된 금속-산화물-금속(MOM) 커패시터(약 5 fF)가 이 효과를 중화하기 위해 사용됩니다[그림 7(b) 참조]. 두 개의 교차 연결된 커패시터는 처리 변동성을 고려한 10비트 사례에서 결합 효과를 1/2 LSB 이하(2.5 fF)로 감소시킵니다. 더 높은 정밀도를 달성하기 위해, 더미 스위치와 더미 라우팅은 결합 효과를 줄이기 위한 대안적인 해결책입니다.

B. Dynamic Comparator with a Current Source
B. Dynamic Comparator with a Current Source
Fig. 8 shows a schematic of the comparator. During the conversion phase, the input voltages of the comparator approach ground. For proper function within the input common-mode voltage range from half Vref to ground, the comparator uses a p-type input pair. Because a dynamic comparator does not consume static current, it is suitable for energy efficient design.
B. 전류원이 있는 동적 비교기
그림 8은 비교기의 회로도를 보여줍니다. 변환 단계 동안 비교기의 입력 전압은 접지에 근접합니다. Vref의 절반부터 접지까지의 입력 공통 모드 전압 범위 내에서 적절한 기능을 위해, 비교기는 p형 입력 쌍을 사용합니다. 동적 비교기는 정적 전류를 소비하지 않기 때문에 에너지 효율적인 설계에 적합합니다.
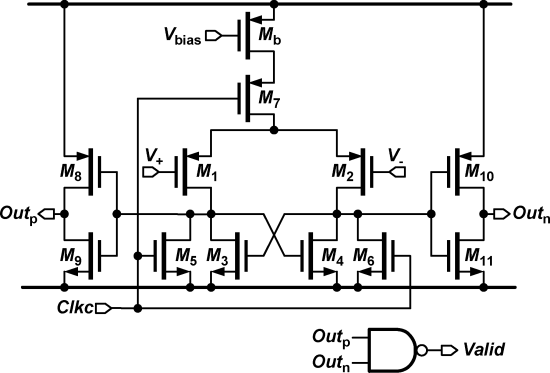
When Clkc is high, the comparator outputs Outp and Outn are reset to high. When Clkc goes to low, the differential pair, M1 and M2, compares the two input voltages. Then, the latch regeneration forces one output to high and the other to low according the comparison result. Consequently, the Valid signal is pulled to high to enable the asynchronous control clock. The offset voltage of this comparator can be expressed as [15]
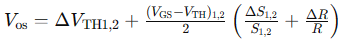
Clkc가 높은 상태일 때, 비교기의 출력 Outp와 Outn은 높은 상태로 리셋됩니다. Clkc가 낮아지면, 차동 쌍인 M1과 M2는 두 입력 전압을 비교합니다. 그런 다음 래치 재생성은 비교 결과에 따라 한 출력을 높게 하고 다른 출력을 낮춥니다. 그 결과, Valid 신호가 높아져 비동기 제어 클록이 활성화됩니다. 이 비교기의 오프셋 전압은 다음과 같이 표현될 수 있습니다 [15]
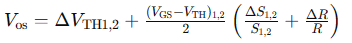
where ΔVTH1,2 is the threshold voltage offset of the differential pair M1 and M2, (VGS−VTH)1,2 is the effective voltage of the input pair, ΔS1,2 is the physical dimension mismatch between M1 and M2, and ΔR is the loading resistance mismatch induced by M3-M6. The first term is a static offset which does not affect the performance of a SAR ADC. However, the second term is a signal-dependent dynamic offset. The effective voltage of the input pair varies with the input common-mode voltage. The dynamic offset degraded the performance of the first prototype [1].
여기서 ΔV_TH1,2는 차동 쌍 M1과 M2의 문턱 전압 오프셋을 나타내고, (V_GS−V_TH)_1,2는 입력 쌍의 유효 전압을 나타내며, ΔS_1,2는 M1과 M2 사이의 물리적 차원 불일치를 나타내고, ΔR은 M3-M6에 의해 유도된 부하 저항의 불일치를 나타냅니다. 첫 번째 항은 SAR ADC의 성능에 영향을 미치지 않는 정적 오프셋입니다. 그러나 두 번째 항은 신호에 따라 변하는 동적 오프셋입니다. 입력 쌍의 유효 전압은 입력 공통 모드 전압에 따라 변합니다. 이 동적 오프셋은 첫 번째 프로토타입의 성능 저하를 초래했습니다 [1].
There are several possible approaches to improve the dynamic offset. The comparator size can be enlarged, which results in larger power consumption. The effective voltage of the input pair can be reduced, but this decreases the comparison speed. The error tolerant non-binary search algorithm [10] is also a feasible method. A simple and reliable way is to cascode a biased MOS (Mb) at the top of the switch MOS, as shown in Fig. 8. Because Mb is in the saturation region, the change of its drain-source voltage has only a slight influence on the drain current. Hence, Mb keeps the effective voltage of the input pair near a constant value when common-mode voltage changes. The dynamic offset thus has a minor influence on the conversion linearity.
동적 오프셋을 개선하기 위한 몇 가지 가능한 접근 방법이 있습니다. 비교기의 크기를 키우는 것은 더 큰 전력 소비를 초래하지만, 입력 쌍의 유효 전압을 줄이는 것은 비교 속도를 감소시킵니다. 오류에 강한 비이진 검색 알고리즘 [10]도 실행 가능한 방법입니다. 간단하고 신뢰할 수 있는 방법은 그림 8에 표시된 것처럼 스위치 MOS의 상단에 편향된 MOS(Mb)를 캐스코드하는 것입니다. Mb가 포화 영역에 있기 때문에 그 드레인-소스 전압의 변화는 드레인 전류에 거의 영향을 미치지 않습니다. 따라서 Mb는 공통 모드 전압이 변할 때 입력 쌍의 유효 전압을 거의 일정하게 유지합니다. 이로 인해 동적 오프셋은 변환 선형성에 미미한 영향을 미칩니다.
C. SAR Control Logic
C. SAR Control Logic
To avoid using a high-frequency clock generator, the proposed ADC uses an asynchronous control circuit to internally generate the necessary clock signals. Fig. 9 shows a schematic and a timing diagram of the asynchronous control logic. The dynamic comparator generates the Valid signal. Clks is the control signal of the sampling switches, it turns on the switches at high potential and turns off the switches at low potential. The sampling phase is about 20% of the whole clock period. Clkc is the control signal of the dynamic comparator. Clk1 to Clk10 sample the digital output codes of the comparator and serve as control signals for the capacitor arrays to perform the monotonic switching procedure.
C. SAR 제어 논리
고주파 클록 발생기를 사용하지 않기 위해 제안된 ADC는 비동기 제어 회로를 사용하여 필요한 클록 신호를 내부적으로 생성합니다. 그림 9는 비동기 제어 논리의 회로도와 타이밍 다이어그램을 보여줍니다. 동적 비교기는 유효 신호(Valid signal)를 생성합니다. Clks는 샘플링 스위치의 제어 신호로, 고전위에서 스위치를 켜고 저전위에서 스위치를 끕니다. 샘플링 단계는 전체 클록 주기의 약 20%를 차지합니다. Clkc는 동적 비교기의 제어 신호입니다. Clk1부터 Clk10까지는 비교기의 디지털 출력 코드를 샘플링하고 커패시터 어레이의 모노토닉 스위칭 절차를 수행하는 제어 신호로 사용됩니다.
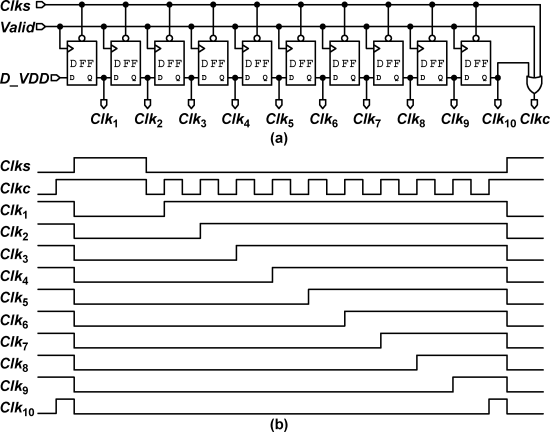
Fig. 10 shows a schematic and a timing diagram of the DAC control logic. At the rising edge of Clki, a static flip-flop samples the comparator output. If the output is high, the relevant capacitor is switched from Vref to ground. If the output is low, the relevant capacitor is kept connected to Vref. At the falling edge of Clki, all capacitors are reconnected to Vref. The delay buffer guarantees that Clki triggers the AND gate after the output of the static flip-flop. This timing arrangement avoids unnecessary transitions. This work uses an inverter as a switch buffer. The conventional architecture in Fig. 1 samples both the input signal and reference voltages on the bottom plates. If the input swing is nearly rail-to-rail, transmission gates are needed to sample input signal. This work uses bootstrapped switches to sample input signal onto top plate of the capacitors and uses inverter buffers to switch between positive and negative voltages. Hence, compared to the conventional architecture, no transmission gates are used, which enables high-speed and low-power operation.
그림 10은 DAC 제어 논리의 회로도와 타이밍 다이어그램을 보여줍니다. Clki의 상승 에지에서 정적 플립플롭이 비교기 출력을 샘플링합니다. 출력이 높으면 관련 커패시터가 Vref에서 접지로 전환됩니다. 출력이 낮으면 관련 커패시터는 Vref에 계속 연결됩니다. Clki의 하강 에지에서 모든 커패시터는 다시 Vref로 연결됩니다. 지연 버퍼는 Clki가 정적 플립플롭의 출력 후 AND 게이트를 트리거하도록 보장합니다. 이 타이밍 배열은 불필요한 전환을 피합니다. 이 작업에서는 스위치 버퍼로 인버터를 사용합니다. 그림 1의 전통적인 구조에서는 입력 신호와 참조 전압을 모두 커패시터의 하단 판에서 샘플링합니다. 입력 스윙이 거의 레일 투 레일에 가까우면, 입력 신호를 샘플링하기 위해 전송 게이트가 필요합니다. 이 작업에서는 부트스트랩 스위치를 사용하여 커패시터의 상단 판에 입력 신호를 샘플링하고, 양극성 및 음극성 전압 사이를 전환하기 위해 인버터 버퍼를 사용합니다. 따라서 전통적인 구조에 비해 전송 게이트를 사용하지 않으므로 고속 및 저전력 작동이 가능합니다.
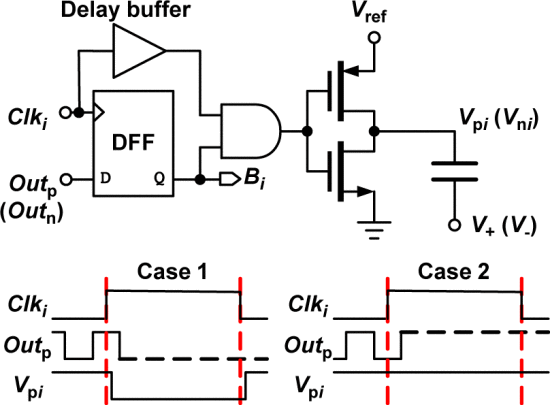
To prevent unnecessary energy consumption and to keep the RC value the same, the sizes of the first six switch buffers are scaled down according to the driven capacitances and the buffers of the last three capacitors are unit size ones.
불필요한 에너지 소비를 방지하고 RC 값을 동일하게 유지하기 위해, 처음 여섯 개의 스위치 버퍼의 크기는 구동되는 커패시턴스에 따라 축소되었으며, 마지막 세 개의 커패시터의 버퍼는 단위 크기입니다.
D. Capacitor Array
D. Capacitor Array
The first prototype used metal–insulator–metal (MIM) capacitors while the revised one uses metal–oxide–metal (MOM) capacitors to construct the capacitor array. Fig. 11(a) shows a sandwich capacitor [5], where the gray part is the top plate. The bottom plate encloses the top plate to minimize the parasitic capacitance. The capacitor consists of only three metals, yielding a small capacitance per unit area. For a SAR ADC, capacitors occupy most of the area. Therefore, increasing the unit capacitance greatly improves the area efficiency.
D. 커패시터 어레이
첫 번째 프로토타입에서는 금속-절연체-금속(MIM) 커패시터를 사용했지만, 개정된 버전에서는 금속-산화물-금속(MOM) 커패시터를 사용하여 커패시터 어레이를 구성합니다. 그림 11(a)는 샌드위치 커패시터[5]를 보여주는데, 회색 부분이 상단 판입니다. 하단 판은 기생 커패시턴스를 최소화하기 위해 상단 판을 감싸고 있습니다. 이 커패시터는 세 개의 금속만으로 구성되어 단위 면적당 작은 커패시턴스를 제공합니다. SAR ADC의 경우, 커패시터가 대부분의 면적을 차지합니다. 따라서 단위 커패시턴스를 증가시키면 면적 효율성이 크게 향상됩니다.
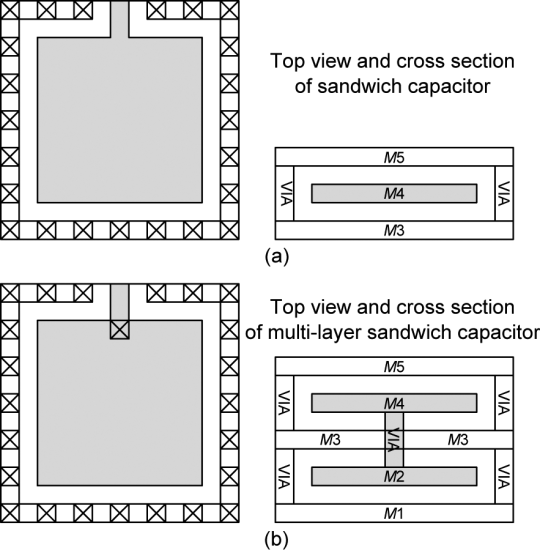
Fig. 11(b) shows a multi-layer sandwich capacitor which doubles the effective capacitor area. The capacitance of a unit multi-layer sandwich capacitor (3.3 μm×3.3 μm) is about 4.8 fF while that of a sandwich capacitor of the same size is only 2.4fF. Therefore, the multi-layer sandwich capacitor is much more hardware efficient. The binary capacitor array of the proposed 10-bit SAR ADC uses 29 unit capacitors. Therefore, the total sampling capacitance of one capacitor network is 2.5 pF. The two capacitor networks occupy a total active area of 195 μm×195 μm, about 72% of the whole ADC.
그림 11(b)는 효과적인 커패시터 면적을 두 배로 늘린 다층 샌드위치 커패시터를 보여줍니다. 한 단위의 다층 샌드위치 커패시터(3.3μm×3.3μm)의 커패시턴스는 약 4.8fF이며, 같은 크기의 샌드위치 커패시터의 커패시턴스는 2.4fF에 불과합니다. 따라서 다층 샌드위치 커패시터는 훨씬 더 하드웨어 효율이 높습니다. 제안된 10비트 SAR ADC의 이진 커패시터 어레이는 29개의 단위 커패시터를 사용합니다. 따라서 하나의 커패시터 네트워크의 총 샘플링 커패시턴스는 2.5pF입니다. 두 커패시터 네트워크는 총 195μm×195μm의 활성 면적을 차지하며, 이는 전체 ADC의 약 72%에 해당합니다.
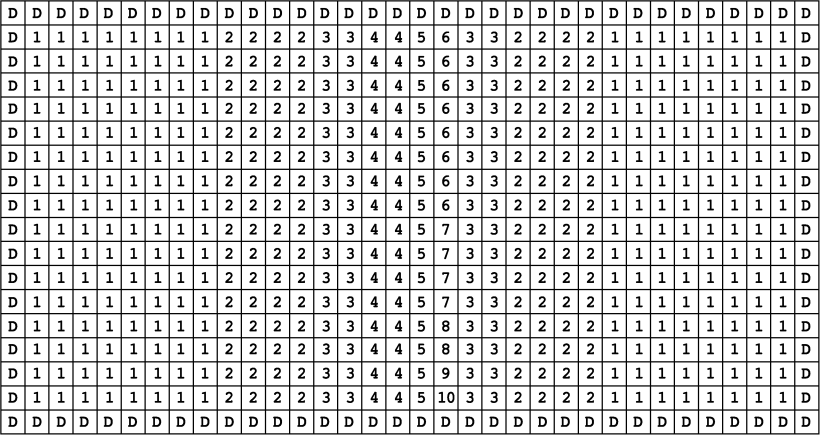
Due to the small unit capacitance, the routing parasitic capacitance has a considerable influence on the ratio of capacitances. The capacitors were placed in an intuitive way to simplify the layout routing. Fig. 12 shows the layout floorplan of the capacitor array.
단위 커패시턴스가 작기 때문에 라우팅 기생 커패시턴스가 커패시턴스 비율에 상당한 영향을 미칩니다. 커패시터 배치는 레이아웃 라우팅을 단순화하기 위해 직관적인 방식으로 이루어졌습니다. 그림 12는 커패시터 어레이의 레이아웃 평면도를 보여줍니다.
논문 링크 : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5437496
A 10-bit 50-MS/s SAR ADC With a Monotonic Capacitor Switching Procedure
ieeexplore.ieee.org